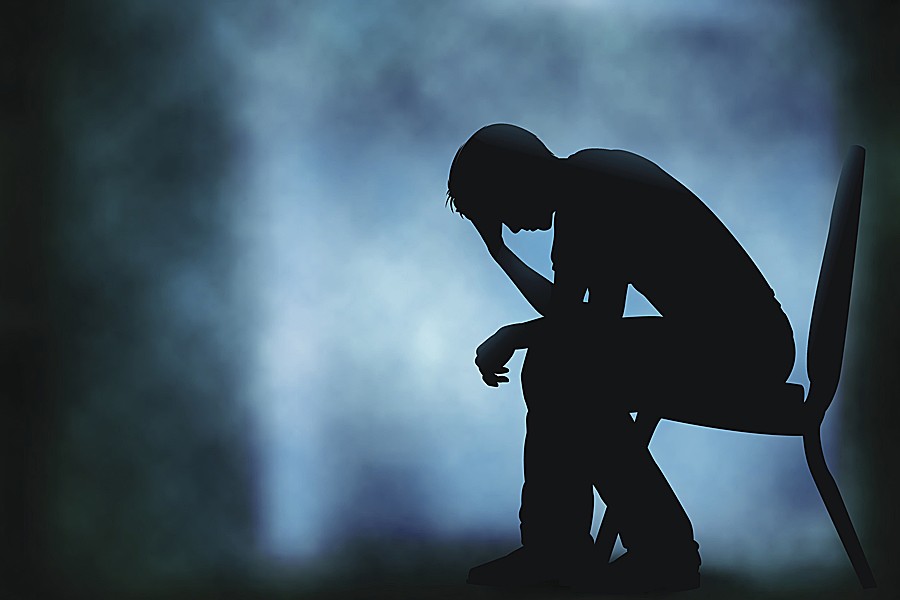
We all go through ups and downs in our mood. Sadness is a normal reaction to life’s struggles, setbacks and disappointments. Many people use the word “depression” to explain these feelings, but depression is much more than just sadness.
Whatever the symptoms, depression is different from normal sadness in that it engulfs your day-to-day life, interfering with your ability to work, study, eat, sleep, and have fun.
The feelings of helplessness, hopelessness and worthlessness are intense and unrelenting, with little, if any, relief.
Some people describe depression as “living in a black hole” or having a feeling of impending doom. However, some depressed people don’t feel sad at all-instead, they feel lifeless, empty, and apathetic.
Signs and Symptoms of Depression
Depression varies from person to person, but there are some common signs and symptoms.
Feelings of helplessness and hopelessness. A bleak outlook—nothing will ever get better, and there’s nothing you can do to improve your situation.
Loss of interest in daily activities. No interest in former hobbies, pastimes, social activities, or sex. You’ve lost your ability to feel joy and pleasure.
Appetite or weight changes. Significant weight loss or weight gain—a change of more than 5% of body weight in a month.
Sleep changes. Either insomnia, especially waking in the early hours of the morning or oversleeping (also known as hypersomnia).
Irritability or restlessness. Feeling agitated, restless, or on edge. Your tolerance level is low; everything and everyone gets on your nerves.
Loss of energy. Feeling tired, sluggish and physically drained. Your whole body may feel heavy, and even small tasks are exhausting or take longer to complete.
Self-loathing. Strong feelings of worthlessness or guilt. You harshly criticise yourself for perceived faults and mistakes.
Concentration problems. Trouble focusing, making decisions or remembering things.
Unexplained aches and pains. An increase in physical complaints such as headaches, back pain, aching muscles, and stomach pain.
The Faces Of Depression
Depression often looks different in men, women, young people and older adults. An awareness of these differences helps ensure that the problem is recognised and treated.
Depression In Teens
While some depressed teens appear sad, others do not. In fact, irritability-rather than depression-is frequently the predominant symptom in depressed adolescents and teens. A depressed teenager may be hostile, grumpy, or quickly lose his or her temper. Unexplained aches and pains are also common symptoms of depression in young people.
Depression In Men
Many men associate depression, however wrongly, with a sign of weakness and excessive emotion. Men tend to complain about fatigue, irritability, sleep problems, and loss of interest in work and hobbies. Other signs and symptoms of depression in men include anger, aggression, violence, reckless behaviour, and substance abuse. Even though depression rates for women are twice as high as those for men, men are at higher suicide risk, especially older men.
Depression In Women
Rates of depression in women are twice as high as they are in men. This is due in part to hormonal factors, particularly when it comes to premenstrual syndrome (PMS), premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD), postpartum depression, and perimenopausal depression. As for signs and symptoms, women are more likely than men to experience pronounced feelings of guilt, sleep excessively, overeat, and gain weight. Women are also more likely to suffer from Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD).
Lifestyle Changes: An Essential Part Of Depression Treatment
Lifestyle changes are not always easy to make, but they can have a significant impact on depression. Take a good look at your lifestyle. What changes could you make to support depression recovery? Self-help strategies that can be very effective include:
Cultivating supportive relationships
Getting regular exercise and sleep
Eating healthily to boost your mood naturally
Managing stress
Practicing relaxation techniques
Challenging negative thought patterns
Causes and Risk Factors for Depression
Loneliness Lack of social support
Recent stressful life experiences
Family history of depression
Marital or relationship problems
Financial strain
Early childhood trauma or abuse
Alcohol or drug abuse
Unemployment or underemployment
Health problems or chronic pain
Are You Depressed?
If you identify with several of the following signs and symptoms, and they won’t go away, you may be suffering from depression.
you can’t sleep, or you sleep too much
you can’t concentrate or find that previously easy tasks are now difficult
you feel hopeless and helpless
you can’t control your negative thoughts, no matter how much you try
you have lost your appetite, or you can’t stop eating
you are much more irritable and short-tempered than usual
you have thoughts that life is not worth living (Seek help immediately if this is the case)
Seek Professional Help
There are many effective treatments for depression, including therapy, medication, and alternative treatments. Learning about your options will help you decide what measures are most likely to work best for your particular situation and needs.
Consider the help of a Mental Health Professional if depression affects your life. They can help you identify the causes of your depression and better manage your mental health.